비강에서 관찰된 연골점액양섬유종 1예
A Case of Chondromyxoid Fibroma Observed in the Nasal Cavity
Article information
Trans Abstract
Chondromyxoid fibroma (CMF) is an extremely rare, benign cartilaginous tumor found in the craniofacial region. It is often misdiagnosed due to its rare occurrence in the nasal and paranasal sinus; moreover, it has similarities with other cartilaginous tumors, showing the same radiologic and histopathologic features. A 62-year-old female consulted our clinic with the chief complaint of a left nasolabial mass of one-month history. The mass was located in the nasal cavity: from there it extended anteriorly to the anterior nasal spine, posteriorly to the end of the hard palate, and laterally to the maxillary sinus. The nasal septum was deviated to the right side due to the mass effect. Complete removal of the mass was conducted via the modified endoscopic Denker’s approach, and the diagnosis of CMF was established. During the 36-month follow-up, no recurrence was observed.
Introduction
A chondromyxoid fibroma (CMF) is a rare, slow-growing, benign cartilaginous tumor that usually arises from the long bone metaphysis of the lower extremity such as the proximal tibia and distal femur [1]. It constitutes less than 1% of all primary bone tumors and approximately 75% occurs in the long bones of the lower extremities [1-3]. Owing to the rare nature of this tumor, a CMF diagnosis can be challenging and often misdiagnosed in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinus [4]. In this article, we report a case of the CMF in the left nasal cavity which was completely removed via a modified endoscopic Denker’s approach without any cosmetic or functional complications.
Case
A previously healthy 62-year-old female consulted our clinic due to a 1-month history of a left nasolabial mass. The patient did not present with any associated symptoms such as nasal obstruction, facial pain, and paresthesia, among others. During examination, a large elastic mass was observed in the left nasolabial area and left anterior nasal floor (Fig. 1). The mass was covered with mucosa with a smooth surface, and microvessels were observed on the surface. The paranasal CT scans revealed an approximately 5-cm-sized heterogeneous enhancing mass with multiple chondroid calcifications at the left anterior nasal cavity. Extensive bony remodeling and erosions were observed in the nasal septum, left maxillary sinus, and nasal floor (Fig. 2). Paranasal MRI demonstrated a well-marginated hypointense soft tissue mass in the left nasal cavity on T1-weighted images and heterogeneous hyperintense lobulated soft tissue mass extending to the maxillary sinus, nasal septum, and nasal floor on T2-weighted images (Fig. 3).
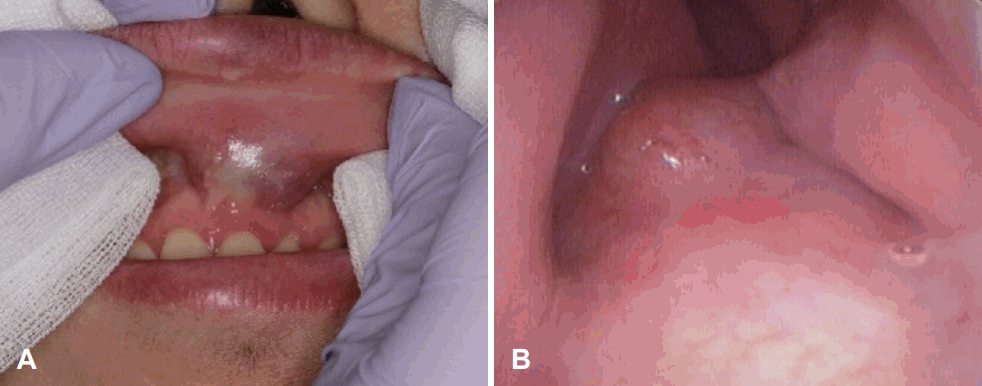
Preoperative physical examination. The swollen area was palpated intraorally; it was movable and tender. A: Endoscopic findings revealed a mass with a smooth surface in the left nasal floor. B: The floor of the nose was swollen and narrowed by a mass inferiorly.
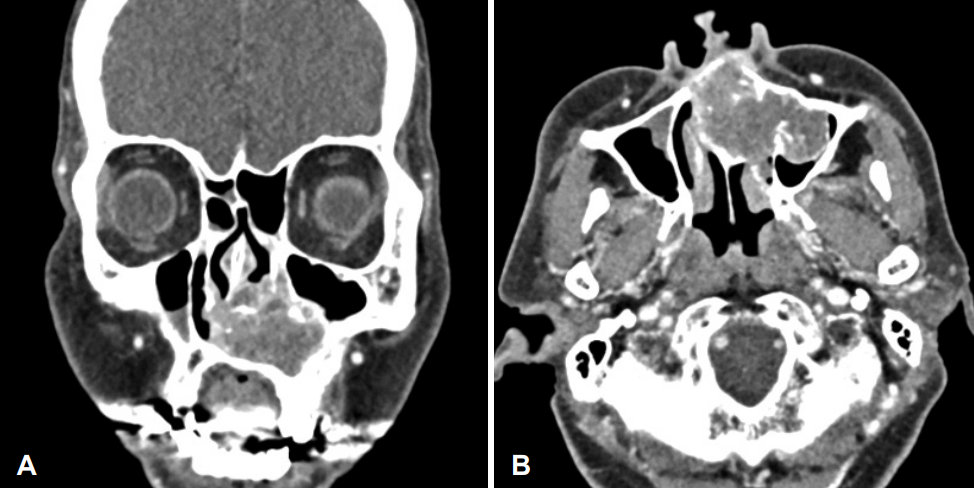
Preoperative contrast-enhanced CT of the paranasal sinus shows a 5-cm expansile heterogenous soft tissue mass with multiple chondroid calcification within the left nasal cavity. A: Coronal view. B: axial view.

Preoperative MRI of the paranasal sinus. A: T1-weighted image reveals a well-marginated hypointense soft tissue mass in the center of the left nasal cavity extending to the nasal septum, medial wall of the maxillary sinus, and nasal floor. B: T2-weighted image shows a well-marginated lobulated hyperintense soft tissue mass with heterogenous enhancement.
Endoscopic resection was performed under general anesthesia. The tumor extended to the anterior nasal spine anteriorly and to the end portion of the hard palate posteriorly. Within the anterior nasal septum, medial involvement was noted, but no extension to the right nasal cavity was noted. Since the lesion was located in the inferior part of the nasal cavity and inside the maxillary sinus, a modified endoscopic Denker’s approach was performed. Together with the tumor, the anterior septal mucosa and cartilage, the anterior part of the inferior turbinate, and the medial wall of maxillary sinus, which were in contact with the tumor, were removed. A postoperative histopathologic examination revealed a lobular growth pattern with stellated or spindle-shaped cells in a prominent myxoid stroma, and a few hyalinized nodules with chondroid differentiation were present. No coagulative tumor necrosis and abnormal mitoses were observed (Fig. 4). Although it is difficult to differentiate between CMF and osteochondromyxoma based on histological findings, considering that most osteochondromyxomas are associated with Carney complex, which is a rare familial syndrome with multiple endocrine neoplasia and lentiginosis, includes osteochondromyxoma as one of its main diagnostic criteria [5]. This case was considered CMF because there were no clinical symptoms associated with Carney complex, such as pigmented skin lesions, hormonal imbalances such as Cushing’s syndrome due to an endocrine tumor, or cardiac symptoms such as palpitations or chest pain due to cardiac myxomas [5]. She was discharged from the hospital 24 h postoperatively without any bleeding or complications. Recurrence was not observed during the 36-month follow-up (Fig. 5).
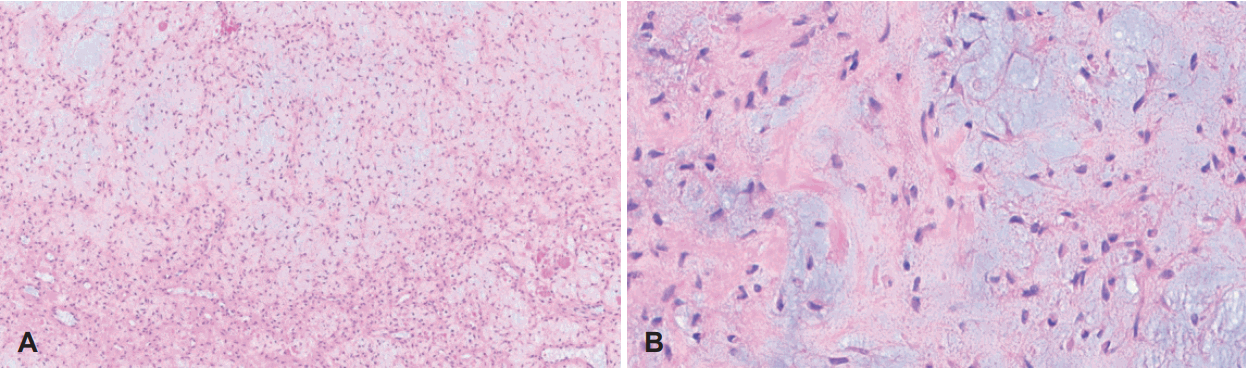
Histopathologic findings. A: Biphasic lobular nature of the tumor with myxoid and cellular area, composed of stellate and spindle-shaped cells (hematoxylin and eosin [H&E] stain, ×100). B: Fibrous spindle cell component shows uniform cells lacking anaplasia (H&E stain, ×400).

Postoperative nonenhanced CT of the paranasal sinus with endoscopic findings. A and B: Coronal (A) and axial (B) scan 2 years post-surgery. A well-healed operative site was observed without recurrence. Septal perforation was still noted. C: However, it did not increase in size compared to immediately after surgery, and mild crusts were noted around it.
Discussion
CMF in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses is extremely rare [6]. Given the rarity of sinonasal CMF and the fact that other chondroid tumors such as chordoma and chondrosarcoma develop more frequently in the craniofacial region, they can be overlooked in the differential diagnosis of bony tumors in these regions [7,8]. Additionally, the clinical symptoms of CMF are non-specific, and various symptoms may present secondary to the mass effect rather than specific to the acute pathology of CMF. Furthermore, the radiographic and histopathological features of CMF are quite similar to those of other cartilaginous tumors. The above rationales preclude early diagnosis and lead to a higher incidence of misdiagnosis [9]. Zillmer and Dorman [2] reported a 22% rate of misdiagnosis of CMF, and He, et al. [10] reported a 100% rate of misdiagnosis in a series of 19 cases.
The presence of calcification on CT should raise suspicion of a cartilaginous or a chondroid matrix-containing lesion. While CMF can have microscopic foci of calcification, these are not often visible on imaging. Conversely, chondrosarcomas typically exhibit prominent calcifications [9]. In this case, a radiologist read the patients’ CT images as chondrosarcoma. Wu, et al. [1] reported that among the 191 tumors, 87% had a purely lucent matrix, while 25 tumors showed some degree of mineralization. MRI provides further information on soft tissue involvement. Typically, CMF presents as a low signal intensity on T1-weighted images and heterogenous high signal intensity on T2-weighted images, often with gadolinium contrast enhancement [1,9,11].
Stellate and spindle-shaped cells arranged in a myxochondroid matrix are the typical microscopic morphology of CMF. These cells exhibit a denser cellularity at the periphery, dividing the loose matrix into pseudolobules, which is observed in approximately 86.7% of cases [1]. Occasionally, the neoplastic cells present with abundant pink cytoplasm, resulting in an epithelioid appearance, which is a feature observed in CMF without a distinctive lobular pattern [1,11]. Osteochondromyxoma can also show a lobular architecture and share common features such as an osteo-chondroid matrix, lack significant atypia, and exhibit sporadically mitotic figures. This highlights the clinical association of osteochondromyxoma with Carney complex, which is an important clue for the diagnosis of such lesion [12]. Pathologically, foci of calcification are typically not prominent (35.3%). However, if present, they can manifest as either granular or coarse form within the lobules. Notably, this type of calcification is a common feature in lesions involving the craniofacial CMF (66.7%) [1]. Although mitotic figures are considered as rare or absent in CMF compared to chondrosarcoma, it may be present in approximately 11.2% of tumors. However, they are not abundant (one to three per 10 high-power fields) [1]. It usually shows positivity for smooth muscle markers, such as S100, CD34, and SOX9, and has a low Ki-67 proliferative rate. Notably, the routine immunohistochemistry examination has a limited value in the differential diagnosis, as vimentin and S100 protein can also be expressed by other cartilaginous tumors [12].
Surgery is the standard treatment of CMF. Due to the high recurrence rate after curettage, wide excision is preferred [2,8]. However, for craniofacial CMF, where en bloc resection can result in functional and cosmetic deformities, some authors recommended curettage followed by close monitoring [13]. Radiation therapy is generally avoided due to the possibility of malignant transformation. But in cases of incomplete excision, postoperative radiation therapy can be used to reduce tumor recurrence [2]. The overall recurrence rate of sinonasal CMF is 17.7%. This rate decreased to only approximately 10% of cases in which gross tumor resection was achieved [6].
Following a case of inferior turbinate origin in 2018, this is the second sinonasal CMF case in Korea [14]. This case was a nasolabial mass which was incidentally discovered and was misconstrued for a simple nasolabial cyst and referred to our hospital for surgery. A nasolabial cyst is often confused with other intranasal masses and could even be an extremely rare tumor such as this case. Since the diagnosis of CMF is very difficult, a comprehensive understanding of not only the clinical symptoms and physical examination findings, but also the radiographic and histopathologic features is warranted to mitigate misdiagnosis.
Acknowledgements
None
Notes
Author contributions
Conceptualization: Sung Jae Heo. Data curation: all authors. Formal analysis: all authors. Methodology: all authors. Supervision: Sung Jae Heo. Validation: Ji Yun Jeong, Sung Jae Heo. Writing—original draft: Minji Oh. Writing—review & editing: Sung Jae Heo.
