Simultaneous Surgical Treatment of Vestibular Schwannoma and Hemifacial Spasm via Minimally Invasive Retrosigmoid Approach
Article information
Abstract
The combination of vestibular schwannoma (VS) and hemifacial spasm (HFS) caused by a vascular loop is not frequently encountered. Surgical intervention using the retrosigmoid approach may enable the two diseases to be treated simultaneously. A 68-year-old male presented with progressive right HFS. MRI revealed a concurrent vascular loop and 3.2-mm intracanalicular VS. The retrosigmoid approach, together with microvascular decompression, was used to remove VS. Intraoperatively, compression by the vascular loop alone induced HFS although it was not related to VS. This finding is in contrast to the literature reports in which VS has been implicated in HFS. In our patient, when VS was completely removed, HFS immediately disappeared postoperatively.
Introduction
Hemifacial spasm (HFS) is a rare clinical condition characterized by involuntary and paroxysmal contraction of the facial muscles. It usually starts by twitching over the orbicularis oculi and later worsens to involve the orbicularis oris, muscles of the cheek, and platysma [1,2]. Primary HFS is caused by vascular compression of the facial nerve within the root entry zone (REZ), whereas secondary HFS is associated with an underlying pathology, such as cerebellopontine angle tumor or vascular malformation [3-5]. Lee, et al. [6] reviewed 2050 cases of HFS and found that only 9 were related to VS, including 6 that were associated with compression by the offending vessels.
Here we report a case in which microvascular decompression (MVD) and VS removal were performed simultaneously via a retrosigmoid approach in a patient with concurrent HFS due to vascular loop and an incidentally detected intracanalicular VS.
Methods
A 68-year-old male presented with right HFS of 4 years duration. The initial spasm consisted of right periorbital twitching, which progressively worsened to involve the right cheek and neck (Supplementary Video 1). The patient had no facial pain, hearing impairment, tinnitus or vertigo. A pure tone audiogram showed high-frequency deterioration with mild sensorineural hearing loss bilaterally (Fig. 1A). MRI revealed a concurrent 3.2-mm enhancing lesion within the right internal acoustic canal (IAC) suggestive of vestibular schwannoma (VS) (Fig. 2A and B). On MRI, the right anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) was in close proximity to the REZ of the ipsilateral facial nerve (Fig. 2C). Despite taking the medication and several previous botulinum toxin A injections, the patient’s symptoms persisted.
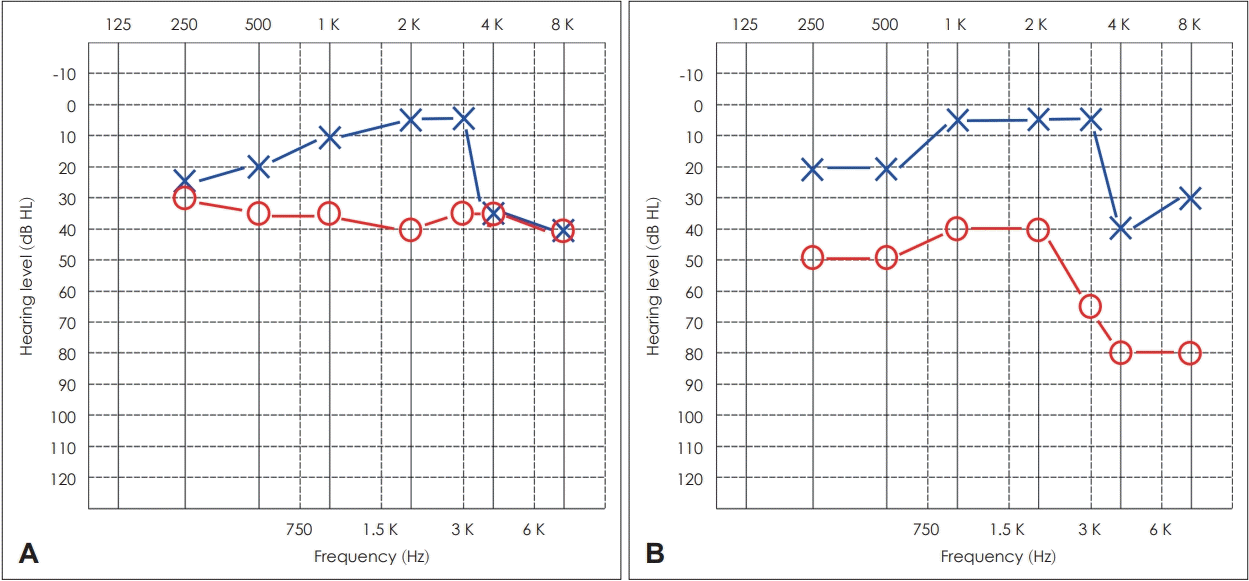
Pre- and post-operative hearing threshold in pure tone audiogram. A: Patient showed 36.3 dB HL threshold in lesion side. B: 3 months after surgery, patients showed 52.5 dB HL. The threshold was increased, but degree of deteroration was acceptable.
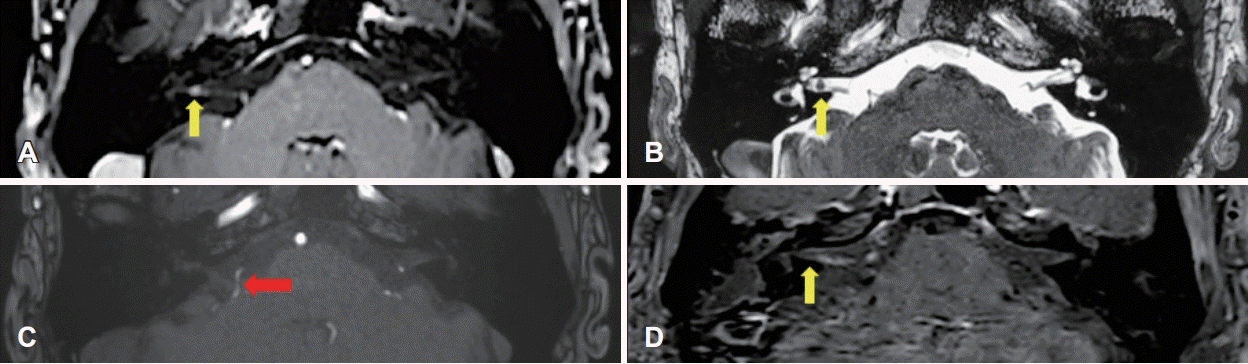
Imaging studies. A and B: Preoperative MRI shows a 3.2-mm vestibular schwannoma within the right internal acoustic canal (yellow arrow). C: Preoperative MR angiogram reveals the right anterior inferior cerebellar artery (red arrow) in close proximity to the root exit zone of the right facial nerve. D: Postoperative MRI confirms complete tumor removal (yellow arrow).
He underwent simultaneous VS removal and MVD of the HFS via an endoscopically assisted minimally invasive retrosigmoid approach [7]. A keyhole opening was made with the patient in the supine position with the head rotated. A small dural opening was made to drain the cerebrospinal fluid, after which the arachnoid membrane was cut and the flocculus was gently retracted. The bony wall of the IAC was drilled to fully expose the VS, which was originated form inferior vestibular nerve and was completely removed while sparing the facial and cochlear nerves (Fig. 3A and B). The AICA was seen to form a loop indenting the facial nerve in the area of the REZ (Fig. 3C). The vessel was dissected off the facial nerve, and MVD then performed by inserting a shredded Teflon sponge between the two structures (Fig. 3D). Facial nerve monitoring was conducted throughout the procedure (Supplementary Video 1).
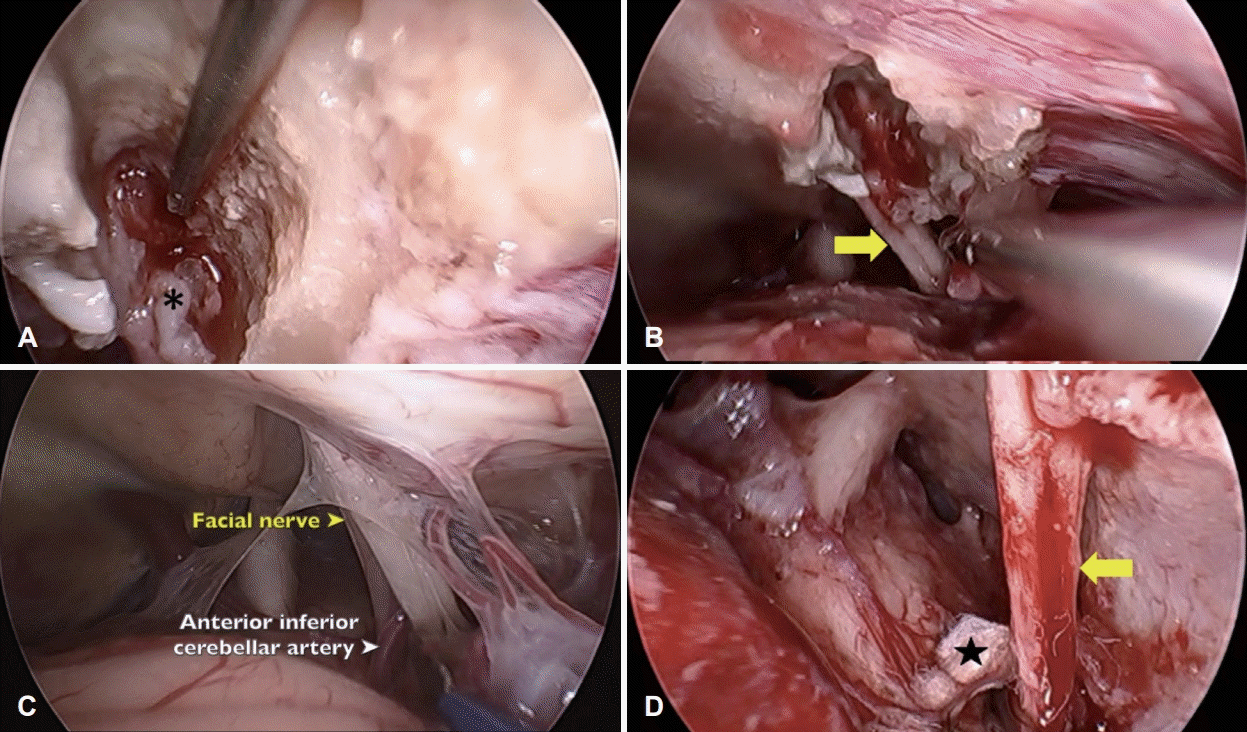
Intraoperative endoscopic findings. A and B: The tumor (*) was originated from inferior vestibular nerve and was confined to the right internal acoustic canal. The tumor was completely removed (yellow arrow) with sparing of facial and cochlear nerve. C: The anterior inferior cerebellar artery (white arrow) loops around the facial nerve. D: A shredded Teflon sponge (★) was placed between the vessel and facial nerve. Part of the vessel is retracted using a micro elevator (yellow arrow).
Postoperatively, repeated MRI showed no evidence of residual tumor in the IAC (Fig. 2D) and hearing deterioration was acceptable (Fig. 1B). The HFS also immediately improved postoperatively (Supplementary Video 1).
Results
The vessel most commonly observed to be compressing the facial nerve at the REZ is the AICA, as in our patient, followed by the posterior inferior cerebellar artery and vertebrobasilar artery and veins [8,9]. HFS in combination with VS is rare, especially when the tumor is intracanalicular [6,10]. The pathophysiology involves irritation of the facial nerve, secondary to direct compression thereof by the tumor at the REZ. The REZ is the site of myelin transition from oligodendrocytes to Schwann cells; moreover, the facial nerve is most susceptible to injury in the REZ, because elsewhere the nerve is protected by the arachnoid mater [1]. Therefore, HFS is less likely to be caused by a intracanalicular tumor, moreover it’s shape and location revealed rare possibility of facial nerve schwannoma.
In our patient, we postulated that HFS was due to vascular loop at the REZ, not to compression by the tumor, because the tumor was only 3.2 mm in diameter and was located at the mid-IAC. We decided to surgically treat the two pathologies simultaneously via the same surgical corridor. Because the patient’s hearing was good preoperatively, a retrosigmoid approach was the most appropriate surgical procedure. Since the tumor was limited to the IAC, a classical large craniotomy was not necessary, while a microscopic approach alone would have been insufficient to deal with the tumor. Thus, an endoscopically assisted minimally invasive retrosigmoid approach was the ideal option for treating both pathologies for experienced surgeon [11].
Compression of the facial nerve at the REZ by the vessel responsible for HFS can be assessed by MRI, which also allows detection of a cerebellopontine angle tumor [12]. This information is important for surgical decision-making. Although HFS does not usually require treatment, surgical intervention should be considered because it may cause severe disfigurement and persistent discomfort to the patient.
The combination of vascular loop and VS in a patient with HFS is uncommon, but the two pathologies can be treated simultaneously. The use of an endoscopically assisted minimally invasive approach enables one-stage surgery via the same surgical corridor.
Supplementary Material
The Data Supplement is available with this article at https://doi.org/10.3342/kjorl-hns.2021.00332.
Video 1.
A patient presented with right periorbital twitching, which progressively worsened to involve the right cheek and neck. An endoscopically assisted minimally invasive retrosigmoid approach allowed vestibular schwannoma removal and microvascular decompression. The patient’s hemifacial spasm immediately disappeared postoperatively.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (NRF-2018R1D1A1A02085472) to I.S.M.
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The Institutional Review Board of the authors’ institution approved this study.
Consent: Written consent taken from the patient.
Notes
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: In Seok Moon. Data curation: In Seok Moon, Khairunnisak Misron. Funding acquisition: In Seok Moon. Methodology: In Seok Moon. Project administration: In Seok Moon. Supervision: In Seok Moon. Validation: Jeong Geum Lee. Visualization: Godlove Mfuko. Writing—original draft: Khairunnisak Misron, Jeong Geum Lee. Writing—review & editing: In Seok Moon. Video editing & narration: Godlove Mfuko.
